Course Introduction (class slides)
CSc 110 Computer Programming I – Course Intro
Welcome to CSc 110
- This is CSc 110, Introduction to Computer Programming I
- Want to learn how to program? . . . You’re in the right class!
Who am I?
- Xinchen Yu (you can call me Xinchen or Dr. Yu)
- Office: Gould-Simpson 854
- Email: xinchenyu@arizona.edu
Who are the teaching assistants? (TAs)
In this course we have course coordinators, senior TAs, and TAs.
The TAs are responsible for:
- Helping you, the students, succeed
- Grading assignments, quizzes, and exams
- Helping students on office hours
. . . So get to know them!
What is this class, anyways?
- In this class, you will learn how to program
- Specifically, programming in Python (version 3)
- Will cover many of the basic principles and concepts that are common to a number of programming languages, such as
- input/output
- conditionals and loops (control flow)
- functions
- data structures
- debugging and more!
The intro sequence
This is the intro course sequence for the CS department:
CSc 101 - Intro to Computer Science
CSc 110 - Intro to Computer Programming I

CSc 120 - Intro to Computer Programming II
General Info
- For some, this is your very first CS course!
- Prerequisites: College Algebra or CSc 101 or appropriate math placement score
Get to know each-other
- Introduce yourself!
- Share your
- Name
- Program/Major, declared or Intended (and why you chose that major)
- One thing that you can do that took many hours of practice
What do you need to succeed in this class?
A willingness to:
- try and fail
- get frustrated and bored
- be curious about how things work
What do you need to succeed in this class?
- Access to a computer with internet (you can get one from the library)
- Install Python and an IDE/editor (Visual Studio Code is recommended)
- Do the readings, watch the videos, come to class, come to lab sessions, come to office hours, do the assignments yourself
How is the structure of this class designed to help you succeed?
- Active learning – you are expected to engage in the in-class activities
- Small sequential steps – each week we build on top of the content of the previous week, make sure you are following along
- Spaced repetition – this is not the type of course you can cram for 2 hours before the exam
- Mastery checks – frequent assessment
Assessment structure
Programming Problems
Short Projects (to be completed in the lab sessions)
Projects
Exams and Quizzes
Exams and Quizzes
Exams are on paper. Why?
- Important skill to develop
- You are able to show what you learned
- Whiteboard coding interviews are common
Exams and Quizzes
- Midterm exams and biweekly quizzes are always on Wednesday (same room as our lectures)
- Our first quiz will be on next Wednesday, Jan 17
Syllabus Activity
- What is the grade distribution for this class?
- How many days you have for regrade requests?
- When are the exams?
Other Important Dates
- Last day for students to add themselves to a course using UAccess is January 17
- Last day for students to drop without a grade of W (withdraw) is January 23
Academic integrity
- You yourself do the work
Examples of breaches of academic integrity:
- Having a friend do the assignments for you
- Using generative AI (for example, ChatGPT) solve the assignments for you
- Copying a solution from the internet
Academic integrity
- TAs are not to debug and give answers
- TAs work with you and answer clarification questions
- Run things on your computer (it will help you with debugging)
- Sharing code is cheating
Materials
- Readings, videos, exercises, slides, assignment instructions will be available on the website
- HOWEVER, you are still responsible for things said/announced in class
How to get help?
Before you ask for help:
- Check for typos (read your error messages)
- Google is your friend (use it wisely). Copy and paste the exact error message on a Google search. (this step also includes read the documentation on the functions you’re trying to use).
How to get help?
Before you ask for help: try rubber duck debugging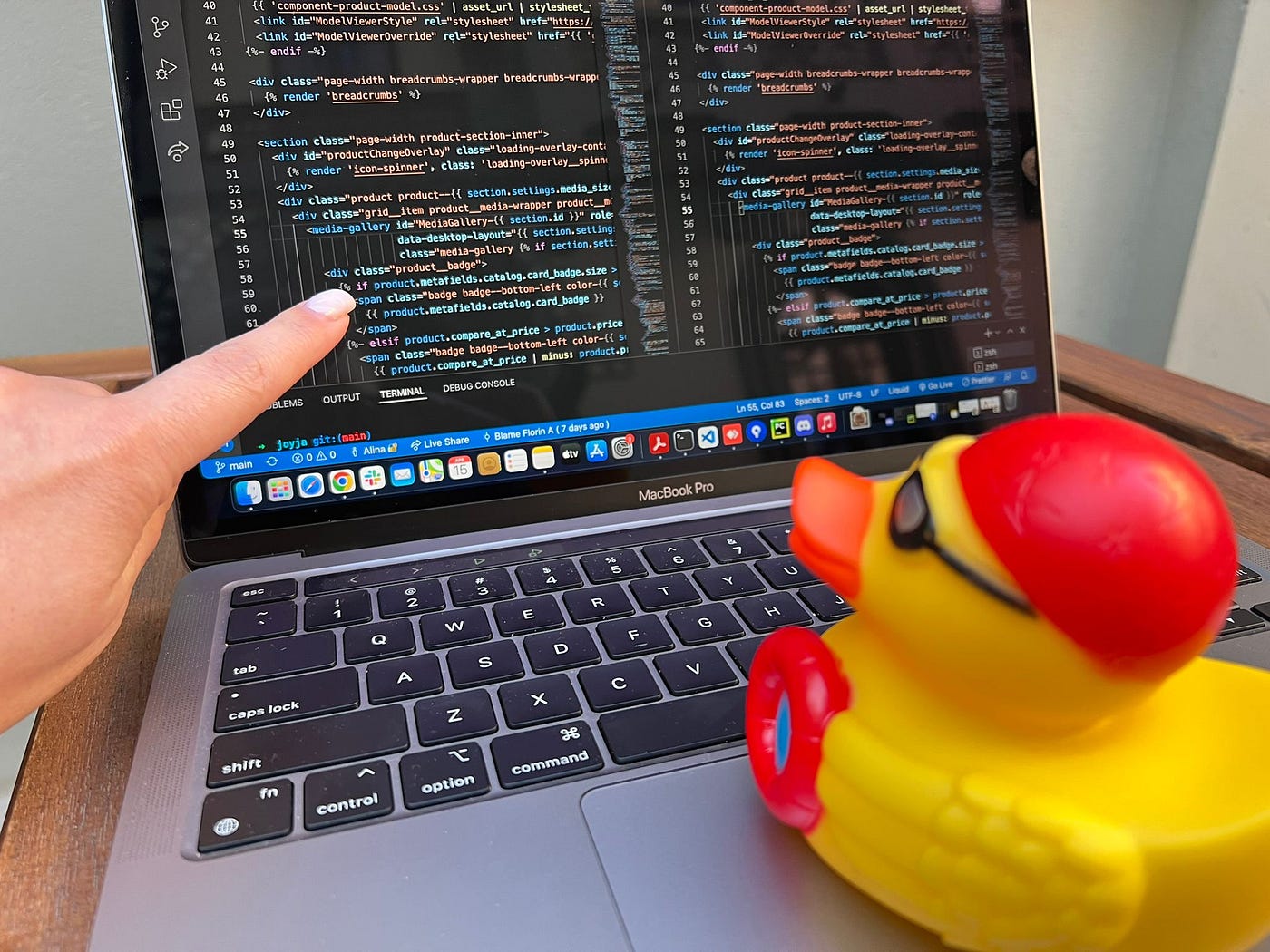 
How to get help?
Before you ask for help: - Try rubber duck debugging.
Describe the problem aloud, explaining it line-by-line, to a rubber duck or another person (who might not have any experience with programming). This is also a good preparation step to asking other people for help (next section).
How to get help?
Once you read your error messages, tried different things, read the Python documentation, and have the line-by-line explanation of what you are trying to do, then ask other people for help.
Be precise and informative.
The more context you can provide about what you’re trying to do and what errors you’re getting, the better.
Also describe the steps you took to try to solve the problem yourself.
How to get help?
- Come to office hours!
But come prepared – do not expect the TAs to solve problems or debug for you (you wouldn’t learn to solve them yourself if you are always asking other people to do it for you)
- 1 point of extra credit if you show up to office hours (read the syllabus for specifics on this)
How to get help?
- Come to office hours!
- Join Piazza and ask questions there
- If you have private questions, generally please make a private Piazza post
- Departmental Tutors (free)
- Do Not email me or TAs